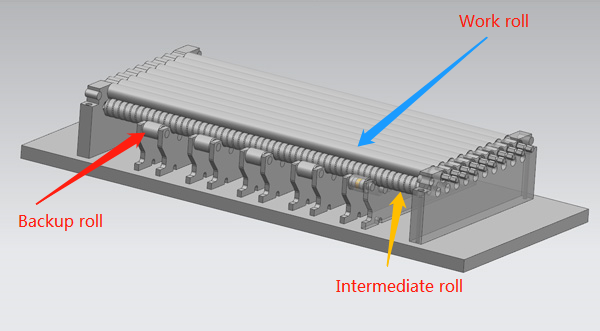
Work rolls for cold rolling mills

Work rolls are the heart of a cold rolling mill. They are the pair of rolls (top and bottom) that make direct contact with the metal strip (usually steel, aluminum, or copper). Their primary function is to apply compressive force to reduce the thickness of the strip by 30-70% in a single pass, while also imparting a desired surface finish and metallurgical properties.
Work rolls operate under extreme conditions, requiring a unique set of properties:
1. Extreme Hardness: Typically 58-65 HRC. Necessary to resist plastic deformation under massive rolling forces (thousands of tons).
2. High Wear Resistance: To maintain precise gauge (thickness) and surface finish over long rolling campaigns.
3. High Toughness: To resist chipping, spalling, and catastrophic failure from thermal and mechanical fatigue.
4. Consistent Microstructure: Usually a fine martensitic matrix with a uniform dispersion of hard carbides (e.g., chromium, vanadium, molybdenum carbides).
5. Precise Dimensional & Geometric Tolerance: Barrel (body) and neck (bearing journal) are machined to micron-level accuracy.
6. Good Thermal Conductivity & Fatigue Resistance: To manage heat generated by deformation and friction.

Material can be 100Cr6, 60CrMoV, 86CrMoV7 as the requirements of customers.
Applications:
• Pickle Lines
• Galvanizing Lines
• Continuous Annealing Lines
• Flatteners
• Heat Treat Levelers
• Plate Mill Levelers
• Steel Processing Lines
• Cut-to-Length Lines
• Aluminum Mills
• Stamping Operations
For more information about work rolls, backup rolls, intermediate rolls, please contact info@lysym-bearing.com.
The applications of SL04 series full complement cylindrical roller bearings

The SL04 series full complement cylindrical roller bearings are designed for extremely high radial load capacity in a compact cross-section. Its primary application is in scenarios where space is limited, and the primary load is pure radial, but where standard caged bearings would be too weak or have too short a service life.
1. Key Design Features of the SL04 Series
To understand its applications, it’s crucial to first understand its design:
Full Complement: This is the most important feature. Unlike standard bearings that use a cage to separate the rollers, “full complement” means the bearing is packed with the maximum number of rollers possible. There is no cage.
High Radial Load Capacity: By eliminating the cage, the bearing can accommodate more rollers, significantly increasing its load-carrying capacity—often by 20-40% compared to a caged version of the same size.
Compact Cross-Section: The SL04 series is part of a “light” or “thin” series. This means its cross-sectional height (the difference between its outer diameter and bore diameter) is smaller than a standard “medium” series bearing. This allows it to fit into compact, weight-sensitive designs.
Limitation: Lower Speed Capability: The lack of a cage is also its main drawback. Without a cage to guide and separate them, the rollers rub against each other during operation, generating significant friction and heat. Therefore, SL04 bearings are not suitable for high-speed applications.
2. Typical Applications
The combination of high load + compact size + low-to-moderate speed makes the SL04 series ideal for the following applications:
1. Gearboxes and Transmissions
This is one of the most common uses.
Location: Often used as planet gear bearings in planetary gearboxes or as support bearings for slow-speed shafts.
Reasoning: Gearboxes, especially in heavy machinery, experience massive radial forces from the meshing of gears. The compact size of the SL04 allows for a more compact gearbox design while handling these high loads. The rotational speeds of the supported components are often low enough to be acceptable for a full complement bearing.
2. Heavy-Duty Machinery and Equipment
Examples: Construction equipment (excavators, cranes), mining machinery, rolling mills, vibratory screens.
Reasoning: These machines are designed to withstand immense loads. Bearings in pivot points, idler wheels, and conveyor pulleys are subjected to severe radial loads but may not rotate very quickly. The SL04’s high load capacity is perfect for this harsh environment.
3. Agricultural Machinery
Examples: Tractors, combines, balers, and other harvesting equipment.
Reasoning: Similar to construction equipment, agricultural machinery requires robust components that can handle shock loads and high radial forces in dirty environments. The simplicity and strength of the SL04 make it a reliable choice.
4. Electric Motors and Generators (Specific Cases)
Usage: Typically used in large, slow-speed motors and generators (e.g., hydroelectric generators, large wind turbine main shafts in some designs).
Reasoning: For very large diameter shafts, the surface speed can be high, but the rotational speed (RPM) is low. The SL04 can support the tremendous weight of the rotor (radial load) effectively at these low RPMs.
5. Material Handling Systems
Examples: Conveyor system rollers, pulley bearings in heavy-load conveying systems.
Reasoning: These bearings support the radial load of the carried material and the belt tension. Speed is typically low, making the SL04 a durable and long-lasting option.
3. Critical Design and Maintenance Considerations
If you are specifying or maintaining an SL04 bearing, pay close attention to these points:
1. Lubrication is CRITICAL: The roller-to-roller contact creates friction that must be managed. A high-quality, high-viscosity lubricant is essential. Grease lubrication is common, but oil lubrication or oil mist systems are often used for better heat dissipation. The lubrication must be continuous and reliable.
2. Misalignment: Like all cylindrical roller bearings, the SL04 series is sensitive to misalignment. The mating shafts and housings must be aligned precisely to prevent edge loading and premature failure.
3. Load Direction: Remember, these are purely radial bearings. They must not be used to support significant axial loads. Any axial load must be handled by a separate thrust bearing in the system.
4. Installation: Care must be taken during installation to avoid damaging the rollers or the raceways, as the rollers are not held in place by a cage.
Sendzimir mill backup bearing|support roller
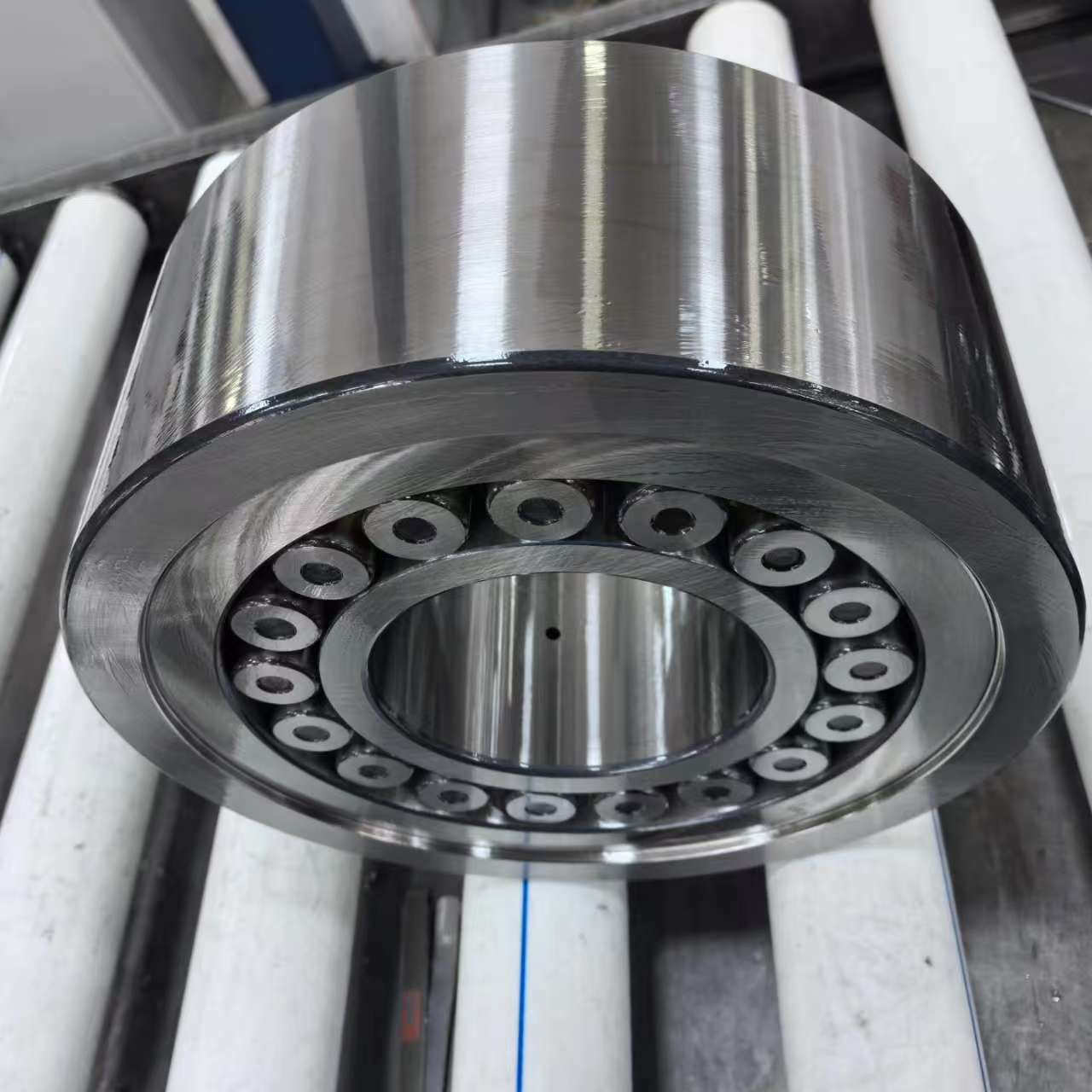

The Sendzimir mill backup bearing or support roller is a critical component in a Sendzimir (Z-mill) rolling mill, which is used for cold rolling thin strips of metal, particularly stainless steel and high-strength alloys. These mills are known for their ability to achieve high reductions with excellent strip flatness control.
Function of Backup Bearings/Support Rollers in a Sendzimir Mill:
In a Sendzimir mill, the work rolls (small-diameter rolls that directly contact the strip) are supported by a cluster of backup bearings (also called support rollers or intermediate rolls). These bearings help:
– Absorb rolling forces to prevent deflection of the work rolls.
– Maintain precise roll alignment for consistent strip thickness.
– Reduce vibration and chatter during high-speed rolling.
– Extend work roll life by distributing load evenly.
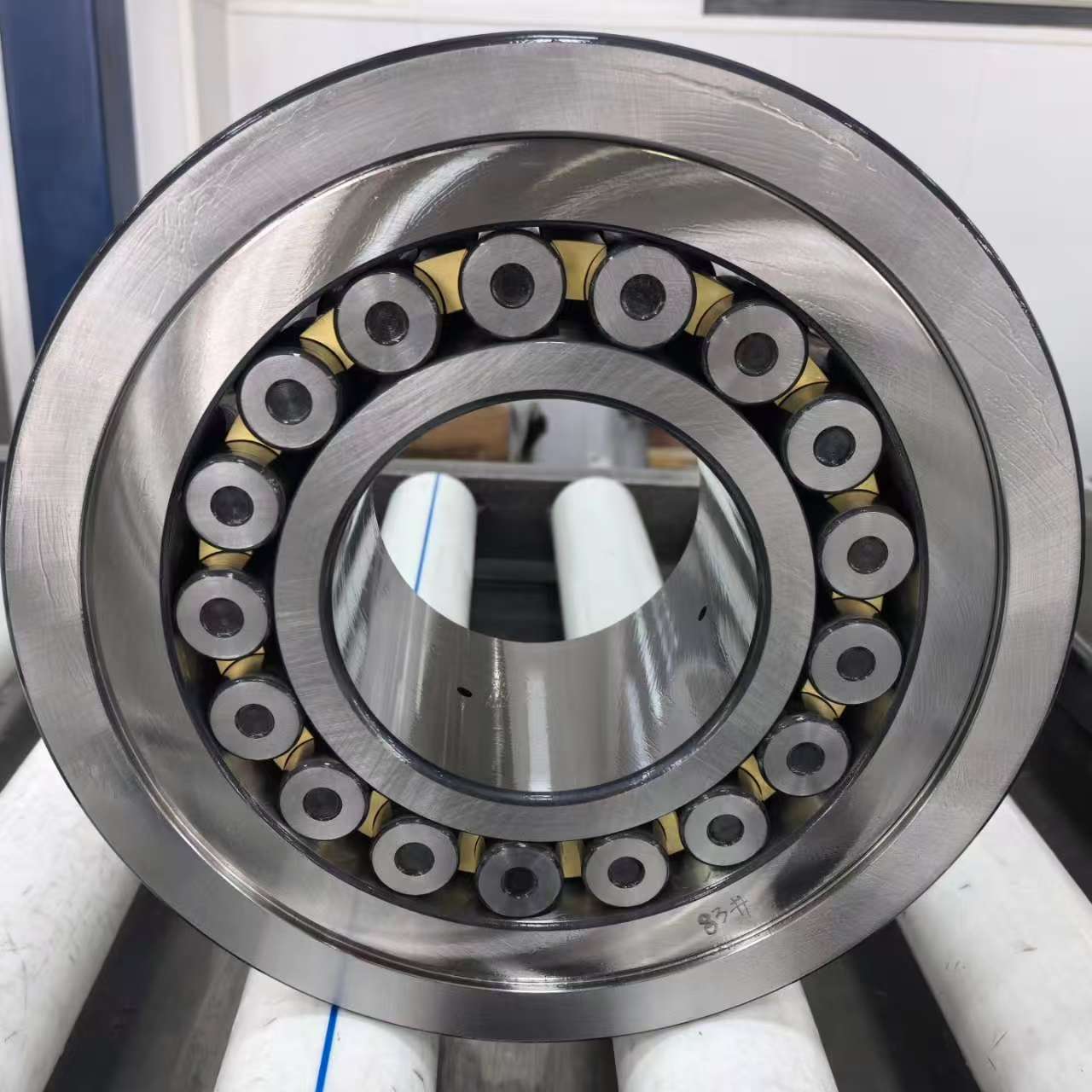

Types of Backup Bearings/Support Rollers:
1. First Intermediate Backup Bearings – Directly support the work rolls.
2. Second Intermediate Backup Bearings– Support the first intermediate bearings.
3. Main Backup Bearings – The largest bearings in the system, absorbing the bulk of rolling forces.
Common Issues & Maintenance:
– Wear & Fatigue: Due to high cyclic loads, backup bearings can develop spalling or brinelling.
– Misalignment: Can cause uneven strip thickness or bearing failure.
– Lubrication Failure: Poor lubrication leads to overheating and premature wear.
– Contamination: Dirt or metal particles can damage bearing surfaces.
Materials & Design Considerations:
– High-grade alloy steel (e.g., bearing steel like 52100 or tool steel) for durability.
– Precision grinding & hardening to ensure smooth operation.
– Advanced sealing systems to prevent lubricant leakage and contamination.
Replacement & Upgrades:
– Regular inspections (vibration analysis, temperature monitoring).
– Using ceramic hybrid bearings for higher speed and longer life.
– Optimized lubrication systems, oil-air or gas systems.
Cooper type split plummer block housings, split pillow block housing
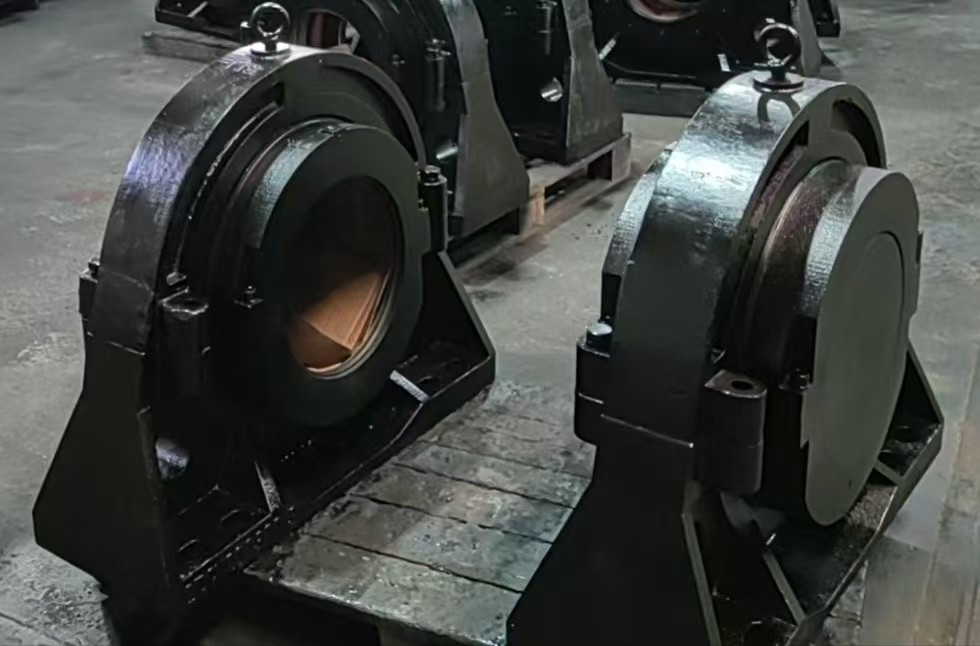

Cooper split plummer block housings are a type of bearing housing designed to support rotating shafts in industrial applications. They are part of the Cooper split bearing series, known for their durability and ease of maintenance. Here’s an overview of their key features and applications:
1. Split Design – The housing is horizontally split, allowing for easy installation and maintenance without removing other components.
2. Material – Typically made from high-quality cast iron (e.g., GG25/GGG40) for strength and vibration damping.
3. Bearing Compatibility – Designed to house spherical roller bearings (SRBs) or self-aligning ball bearings, accommodating misalignment and heavy loads.
4. Sealing Options – Available with various sealing arrangements (labyrinth seals, grease purged seals, etc.) to prevent contamination.
5. Lubrication – Fitted with grease nipples for easy relubrication, ensuring long bearing life.
6. Mounting – Comes with a solid base for bolted mounting onto machinery frames or foundations.
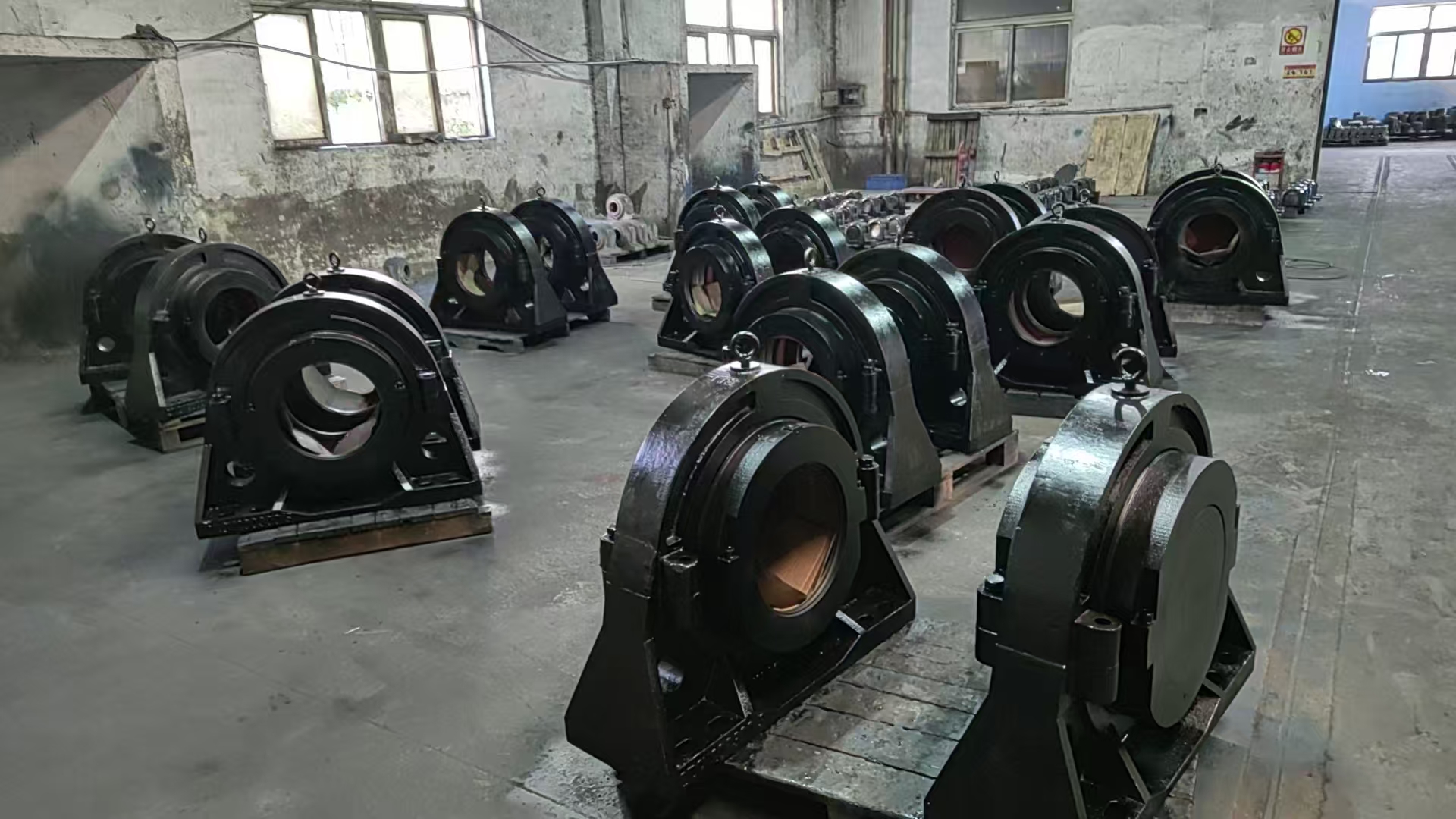

Common Applications:
– Conveyor systems
– Pumps and compressors
– Fans and blowers
– Mining and cement equipment
– Paper and steel mill machinery
Advantages:
Easy Maintenance – Split design allows quick bearing inspection and replacement.
Robust Construction – Suitable for heavy-duty and high-load environments.
Self-Aligning Capability – Compensates for shaft misalignment, reducing wear.
Pressure Roller Bearings in Sinter Plants: Critical Components for Pallet Car Operations
Pressure Roller Bearings in Sinter Plants: Critical Components for Pallet Car Operations
In industrial settings such as sinter plants, where heavy machinery operates under extreme conditions, pressure roller bearings play a pivotal role in ensuring reliability, efficiency, and longevity of equipment. This article explores the application of pressure roller bearings in sinter plants, with a focus on their critical function in pallet cars, which are integral to the sintering process.
1. Understanding Pressure Roller Bearings
Pressure roller bearings, also known as tapered roller bearings or cylindrical roller bearings, are designed to handle both radial and axial loads. Their unique structure-comprising an inner ring, outer ring, tapered rollers, and a cage—enables them to withstand high-pressure conditions while minimizing friction. These bearings are widely used in heavy-duty applications, including mining, steel production, and material handling systems like those in sinter plants.
2. Role of Pallet Cars in Sinter Plants
In a sinter plant, pallet cars are specialized vehicles that transport raw materials (e.g., iron ore fines, coke, and fluxes) through the sintering process. The sintering machine consists of a continuous loop of pallet cars that move along a track, carrying the raw mix through ignition furnaces, cooling zones, and discharge points. During this process, the materials are fused at high temperatures (up to 1,300°C) to form sintered agglomerates, a crucial feedstock for blast furnaces.
Pallet cars operate in harsh environments characterized by:
– Extreme heat from sintering furnaces.
– Heavy loads due to the weight of materials and equipment.
– Dust and abrasive particles generated during material handling.
– Continuous vibration from the movement of the sintering machine.
3. Application of Pressure Roller Bearings in Pallet Cars
Pressure roller bearings are indispensable for the smooth operation of pallet cars. They are typically installed in the following critical areas:
– Wheel assemblies: Bearings support the wheels of pallet cars, enabling them to move smoothly along the track under heavy loads.
– Drive mechanisms: Bearings reduce friction in gearboxes and drive shafts, ensuring efficient power transmission.
– Guide rollers: These bearings maintain alignment and stability as pallet cars navigate curves and inclines.
Key design considerations for pressure roller bearings in sinter plants include:
– High-temperature resistance: Bearings must retain structural integrity and lubrication properties even when exposed to radiant heat from sintering furnaces. Special heat-resistant alloys or ceramic coatings are often employed.
– Dust and contamination protection: Sealed bearings or labyrinth seals prevent ingress of abrasive sinter dust, which can accelerate wear.
– Load capacity: Bearings must support the combined weight of the pallet car, sinter mix, and thermal stresses. Reinforced cages and larger roller diameters are common solutions.
– Lubrication systems: Automatic lubrication systems or high-temperature greases are used to ensure continuous performance under demanding conditions.
4. Challenges and Solutions
The harsh operating environment of sinter plants poses significant challenges for pressure roller bearings:
– Thermal expansion: Temperature fluctuations can cause bearing components to expand or contract, affecting clearance and alignment. Precision engineering and thermal compensation designs mitigate this issue.
– Abrasive wear: Sinter dust infiltrating bearings leads to premature failure. Advanced sealing technologies, such as multi-layered seals or air-purge systems, are critical.
– Fatigue failure: Cyclic loading from continuous operation necessitates bearings with high dynamic load ratings and fatigue-resistant materials like case-hardened steel.
5. Maintenance and Monitoring
Proactive maintenance is essential to maximize bearing lifespan in pallet cars:
– Regular inspections: Visual checks for wear, misalignment, or lubrication deficiencies.
– Vibration analysis: Detects early signs of bearing damage, such as spalling or brinelling.
– Thermal monitoring: Infrared cameras identify overheating bearings caused by inadequate lubrication or excessive friction.
– Lubrication management: Scheduled relubrication with high-temperature greases reduces wear.
6. Case Study: Enhancing Pallet Car Reliability
In a modern sinter plant, upgrading to advanced pressure roller bearings with hybrid ceramic rollers (steel races with ceramic rolling elements) reduced downtime by 30%. The ceramic components offered superior heat resistance and reduced friction, while integrated sensors enabled real-time condition monitoring. This innovation improved pallet car efficiency and extended maintenance intervals.
7. Conclusion
Pressure roller bearings are unsung heroes in sinter plants, enabling pallet cars to operate reliably under extreme conditions. Their design, material selection, and maintenance protocols directly impact the productivity and cost-effectiveness of the sintering process. As sintering technology evolves, advancements in bearing materials (e.g., graphene-enhanced lubricants, smart bearings with IoT connectivity) promise to further enhance performance in this critical industrial application.
By prioritizing robust bearing solutions, sinter plants can achieve higher throughput, reduced energy consumption, and lower operational costs—key factors in the competitive steel manufacturing industry.
Crane Sheave Bearing SL04170PP, Full Complement Cylindrical Roller Bearing
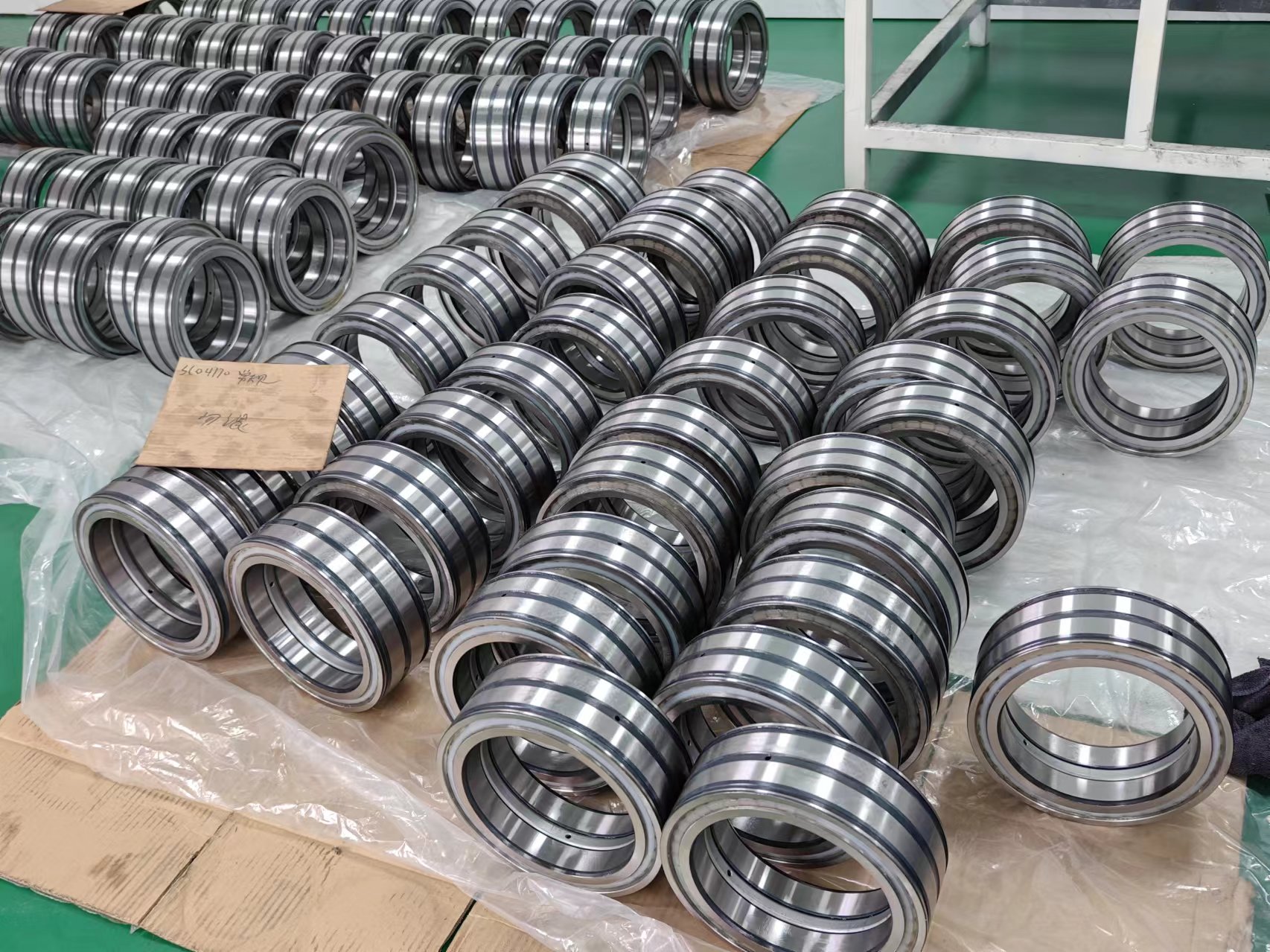

SL04170PP Sheave Bearing 2 Rows Full Complement Bearings with rubber contact seals
ID (inner diameter)/Bore: 170mm
OD (outer diameter): 230mm
Width/Height/thickness: 80mm
Dynamic load rating Cr: 99,500 N
Static load rating Cor: 158,000 N
Spring Bush Bearings: A Resilient Solution for Industrial Applications
Introduction
Spring bush bearings, also known as spring roller bearings, find widespread use in various applications. One of the most typical areas of application is the steel industry. These bearings are employed in various components, including:
- Rollers in Steel Mills: In rolling mills, spring bush bearings support the rollers that shape and process steel sheets.
- Continuous Casting Machines: Spring bush bearings are used for supporting the guide rollers and directing rollers in continuous casting machines.
-
Furnace Equipment: Inside furnaces or refining equipment, spring bush bearings are utilized for the rollers that handle hot materials.
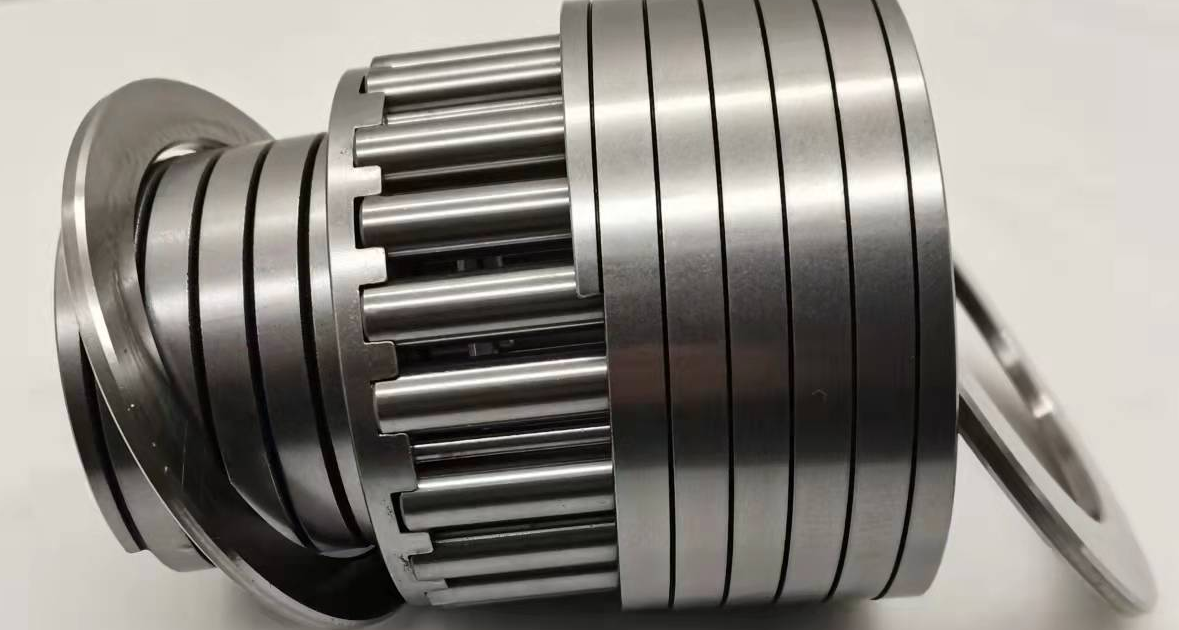 Construction and Components
Construction and ComponentsThe construction of spring bush bearings is relatively straightforward. They consist of three main components:
- Inner Ring: The inner ring provides the mounting surface for the bearing.
- Rolling Elements: These typically include cylindrical rollers with a retaining cage. The rolling elements facilitate smooth rotation.
- Outer Ring: The outer ring encloses the entire assembly and provides stability.
These basic elements can be assembled to create various types of bearings, depending on specific requirements. Whether the application involves split bearing housings, high-temperature operations, or axial load transmission, spring bush bearings can adapt. They handle impact loads and minor misalignments with ease, making them versatile even when multiple challenges arise simultaneously. Additionally, these bearings exhibit excellent wear resistance.
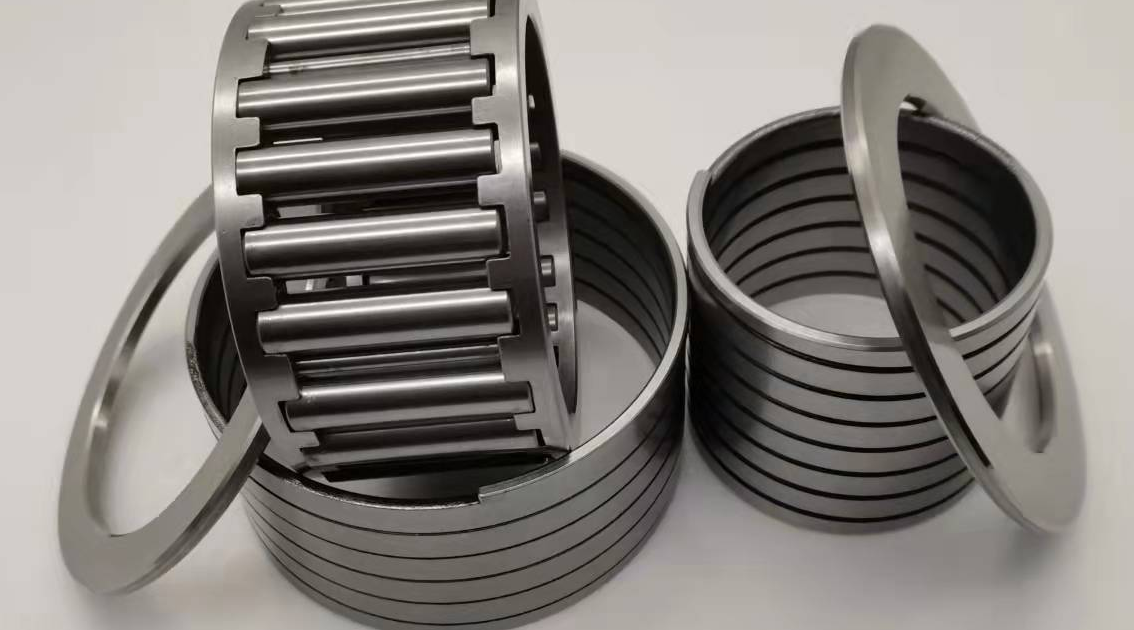

Elasticity and Tolerance
One notable feature of spring bush bearings is their inherent elasticity. The slight clearance between the inner and outer rings allows them to maintain functionality even under conditions like bending deformation. This property makes them particularly suitable for continuous casting machines and high-temperature transfer equipment.
Advantages of Spring Bush Bearings
- Robust Design: Spring bush bearings share a similar height profile with needle roller bearings but offer greater durability. They can withstand temperature variations, contamination, and inadequate lubrication.
- Tolerance to Deviations: These bearings tolerate deviations and inclinations, making them ideal for challenging environments.
-
Application Range: Spring bush bearings find applications beyond the steel industry. They are also used in mining, cement, and other heavy-duty sectors.
Backup Rollers for Levelling Lines: Enhancing Precision and Performance
In the intricate world of metal processing, where precision and efficiency are paramount, backup rollers play a crucial role. These unassuming components provide essential support to tension levelers and metal flattening machines, ensuring optimal performance and consistent results.
Types of Backup Rollers
Full Complement Style:
These backup rollers feature a cylindrical design with a full complement of rollers.
Advantages:
High load capacity (both dynamic and static).
Robust support for axial loads.
Grease lubrication system.
Efficient sealing to prevent contamination.
Ideal for applications where load-bearing capacity is critical.
Roller Cage Style:
Constructed with roller cages made of mold steel or brass.
Advantages:
Wide working surface for increased flattening performance.
High-speed operation.
Strong axial load support.
Pre-lubricated and sealed.
Represents an advanced series of backup rollers.
Precision and Customization
Precision Class: Backup rollers are typically manufactured with precision class P0, but precision classes P6 or P5 can be requested.
Custom Designs: Special designs can be produced upon request to meet specific application requirements.
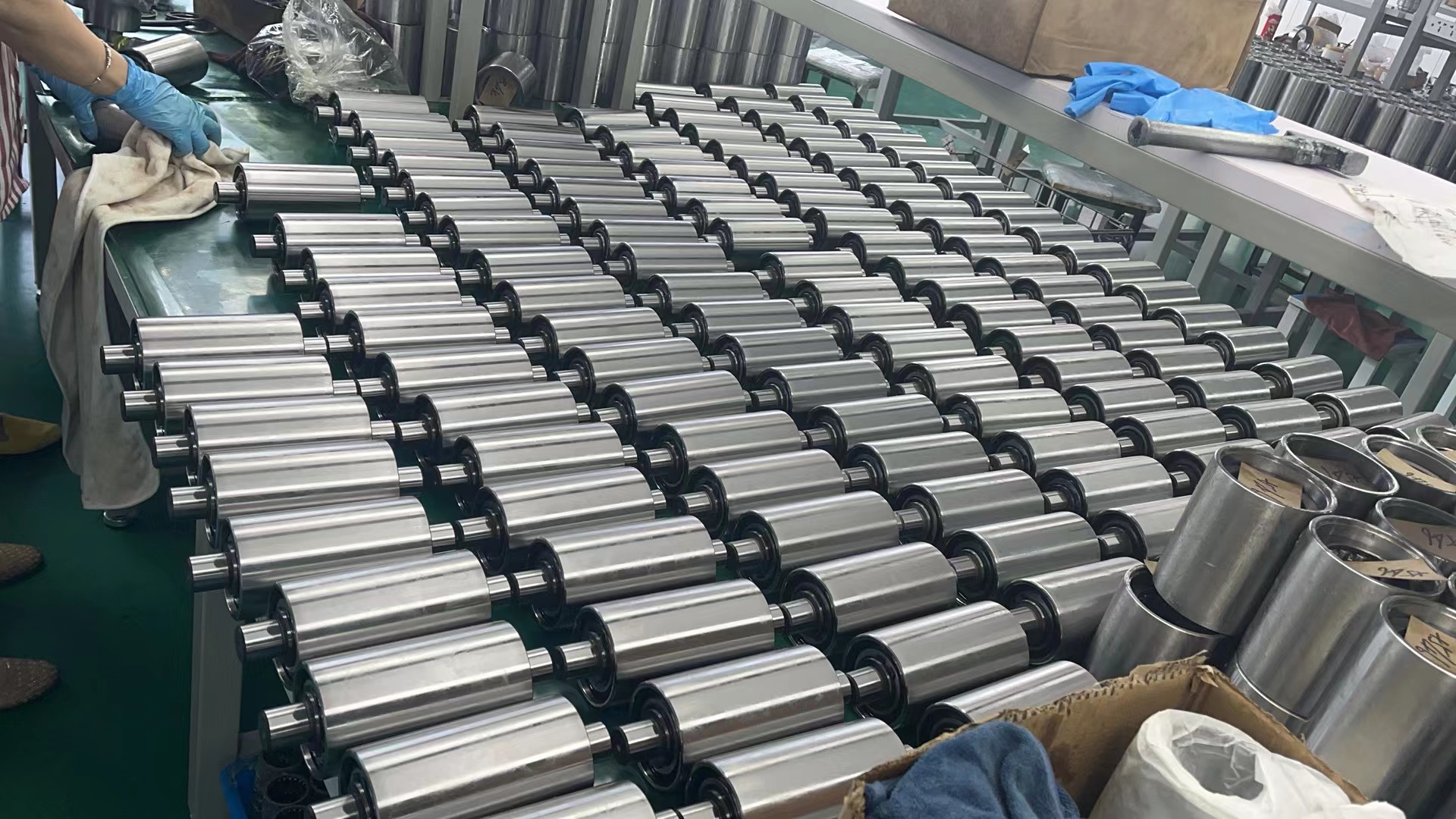

Applications and Beyond
Tension Levelers: Backup rollers ensure stable material processing during tension leveling, preventing work roll deflections.
Metal Flattening Machines: These rollers contribute to consistent sheet flatness and quality.
Spiral Pipe Mills: Forming roller bearings (similar to yoke-type track rollers) are used in spiral pipe mills.
While backup rollers may not grab headlines, their impact on metal processing is undeniable. From maintaining sheet flatness to supporting axial loads, these unheralded heroes keep the industry rolling smoothly. So, next time you admire a perfectly leveled metal sheet, remember the unsung backup rollers that made it possible!
Pressure roller bearing used for pallet cars in sinter plant
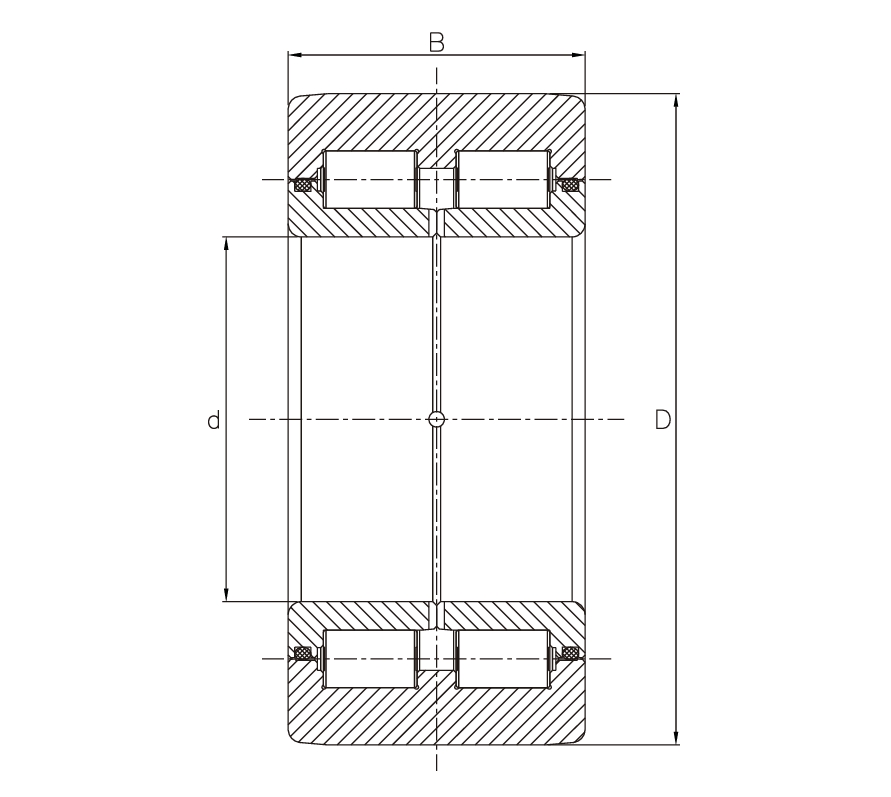
The pressure roller bearings are mainly used in the continuous furnaces of sintering plants. They are massive bearings ready to be fixed. They are used with heavy loads and where the rotation reverses continuously at low speed.
The outer ring shows three entire borders, one section and one outer surface which is highly resistant to wear.
The inner ring is made of two parts, each one has an entire border expressly developed in order to bear high axial thrusts, in addition to radial loads.
Pressure roller bearings do not need maintenance.
The outer ring and the inner ring are manufactured in GCr18Mo steel.
Hardness 60-2 HRC.
In order to increase the resistance to wear, pressure roller bearings usually undergo bainitic temper treatment up to 250° C, named S2.
The sealing system foresees the presence of Viton O-rings, which are inserted in the proper grooves on the inner ring. The seals allow the bearing to be disassembled, they prevent the entrance of contaminating agents and in the meantime, the leakage of lubricant.
| Code | d | D | B | Load ratings | |
| C (KN) | Co (KN) | ||||
| PRB88x170x95 | 88 | 170 | 95 | 384 | 908 |
| PRB93x170x95 | 93 | 170 | 95 | 384 | 908 |
| PRB93x171x95 | 93 | 171 | 95 | 384 | 908 |
| PRB110x200x90 | 110 | 200 | 90 | 414 | 841 |
| PRB110x210x110 | 110 | 210 | 110 | 479 | 942 |
| PRB110x300x87/133 | 110 | 300 | 87/133 | 604 | 1022 |
| PRB120x190x130 | 120 | 190 | 130 | 580 | 1570 |
| PRB120x210x113.8 | 120 | 210 | 113.8 | 584 | 1268 |
| PRB120x210x114 | 120 | 210 | 114 | 584 | 1268 |
| PRB128.665x210x101.6 | 128.665 | 210 | 101.6 | 393 | 1132 |
| PRB128.665x210x114 | 128.665 | 210 | 114 | 463 | 1395 |
| PRB130x210x132 | 130 | 210 | 132 | 529 | 1659 |
| PRB130x250x132 | 130 | 250 | 132 | 899 | 1664 |
| PRB140x250x114 | 140 | 250 | 114 | 769 | 1601 |
| PRB140x250x130 | 140 | 250 | 130 | 899 | 1957 |
NUTR17 yoke type track roller bearing-LYSYM Bearing
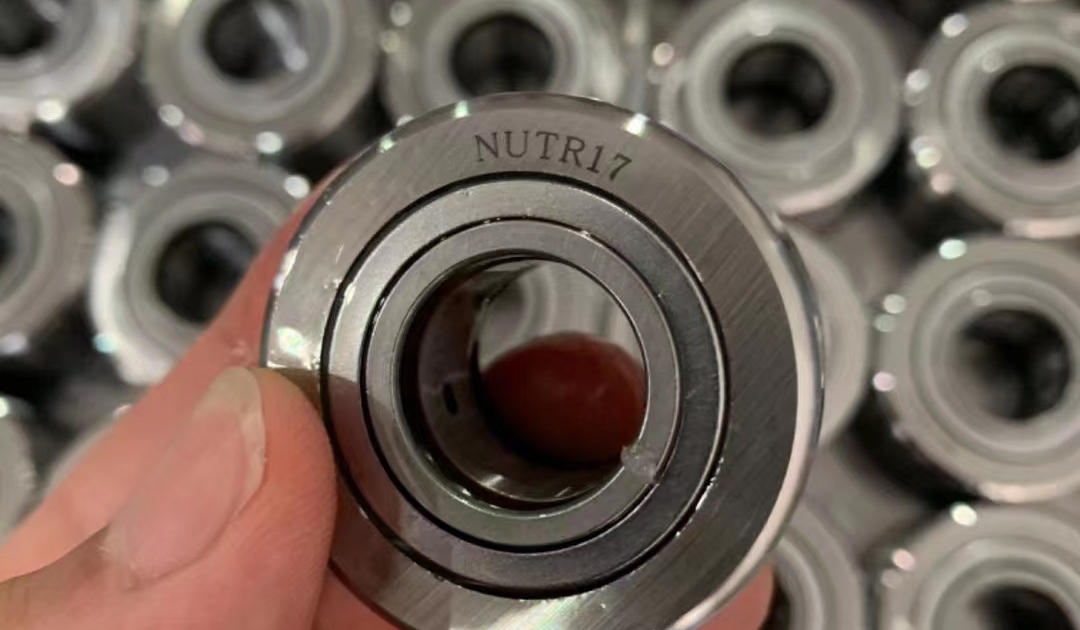

NUTR17 full complement roller yoke type track roller bearing can support very high radial and axial loads due to the double row design. This kind of bearing mainly used for cam drives, slideways, conveying equipment etc.
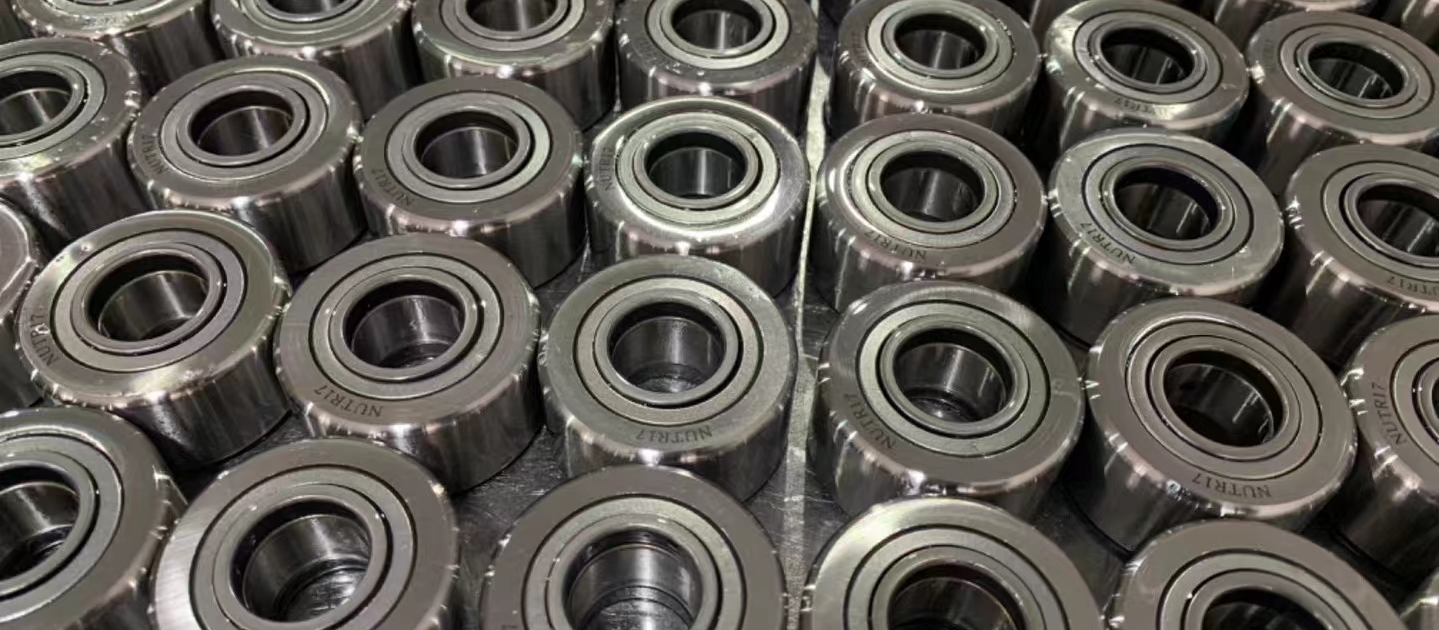

Inside Dimension: 17mm
Outside Dimension: 40mm
Width :21mm

